RMM Tools Weaponized: How Cybercriminals Exploit Remote Management Software
RMM Tools Weaponized: How Cybercriminals Exploit Remote Management Software
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools have become essential for IT departments, enabling them to efficiently manage and support systems remotely. However, this convenience has also created a new attack vector for cybercriminals. Threat actors are increasingly weaponizing RMM tools to gain unauthorized access to systems, steal data, and deploy malware, including ransomware. This article explores how these attacks occur and what you can do to protect your organization.

MSP RMM Solutions: A Full Guide to Remote Monitoring & Management
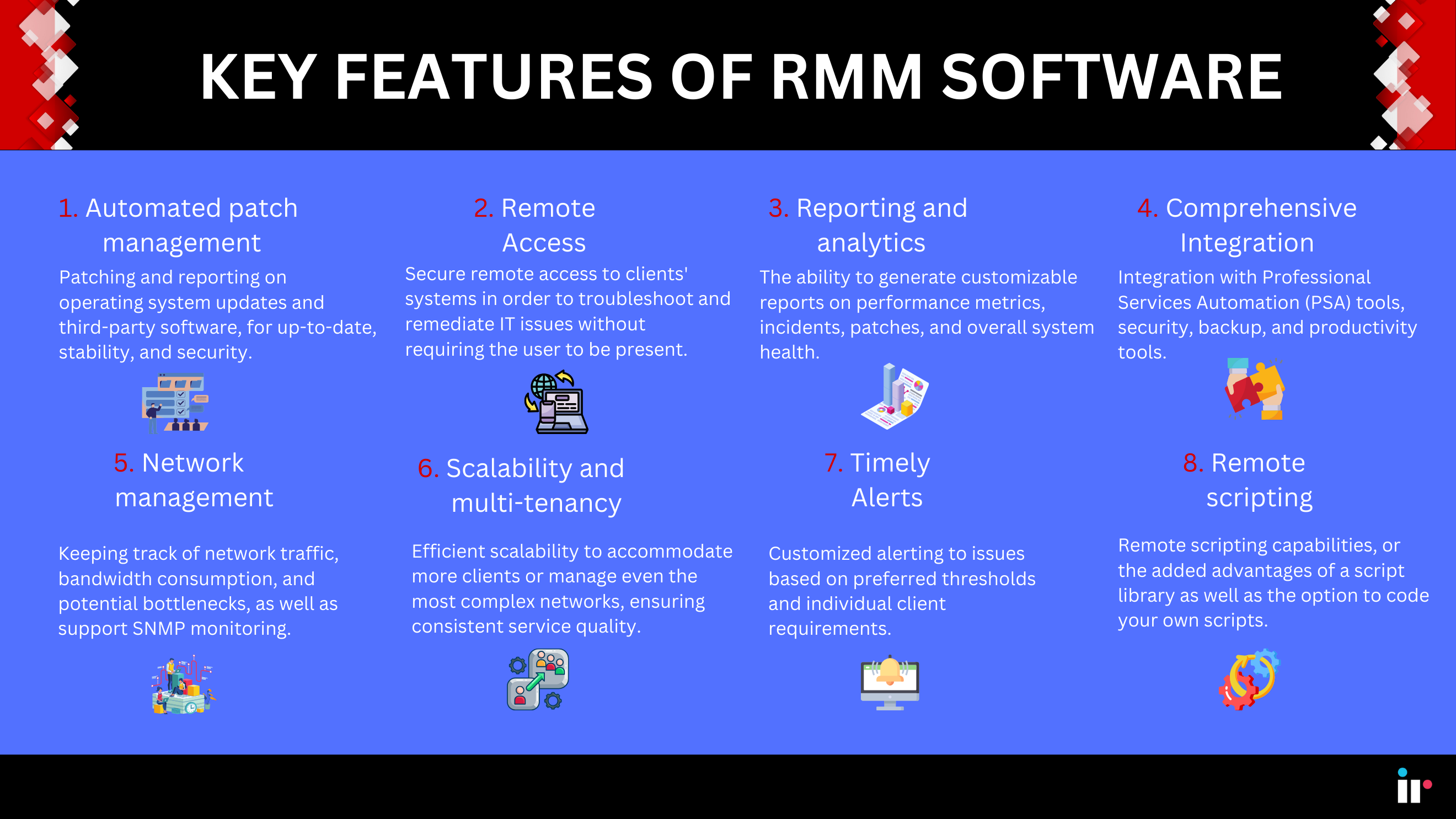
What are RMM Tools?
RMM tools are software solutions designed to help IT professionals remotely monitor, manage, and support computer systems and networks. These tools typically offer features such as:
- Remote access and control
- Software deployment and patching
- System monitoring and alerting
- Automation of routine tasks
- Endpoint security management
Popular RMM tools include AnyDesk, ScreenConnect, PDQ Deploy, and SimpleHelp. While these tools are invaluable for legitimate IT operations, their powerful capabilities can be abused by malicious actors.
How Threat Actors Weaponize RMM Tools
Threat actors are exploiting RMM tools in several ways:
- Gaining Initial Access: Attackers may use phishing emails or other social engineering tactics to trick users into installing malicious RMM agents. These agents provide the attackers with remote access to the compromised system.
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities: Some RMM tools have known vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access. Keeping your RMM software up to date is crucial.
- Compromising MSPs: Managed Service Providers (MSPs) often use RMM tools to manage their clients' systems. If an attacker compromises an MSP's RMM platform, they can potentially access all of the MSP's clients.
- Lateral Movement and Persistence: Once inside a network, attackers can use RMM tools to move laterally to other systems and maintain persistence, even after the initial intrusion is detected.
The Risks and Consequences
The consequences of RMM tool weaponization can be severe:
- Data Breach: Attackers can use RMM tools to access and steal sensitive data.
- Ransomware Attacks: RMM tools can be used to deploy ransomware across an entire network, encrypting files and demanding a ransom for their release.
- System Disruption: Attackers can use RMM tools to disrupt business operations by disabling systems or deleting critical data.
- Reputational Damage: A successful attack can damage an organization's reputation and erode customer trust.
How to Protect Your Organization
Here are some steps you can take to protect your organization from RMM tool weaponization:
- Implement Strong Authentication: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all RMM tool accounts.
- Keep Software Up to Date: Regularly update your RMM software and all other software on your systems to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Monitor RMM Tool Usage: Implement monitoring and alerting to detect suspicious activity, such as unusual login attempts or unauthorized software deployments.
- Restrict Access: Limit access to RMM tools to only those who need it. Use the principle of least privilege.
- Educate Users: Train users to recognize and avoid phishing emails and other social engineering tactics.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Segment your network to limit the impact of a potential breach.
- Use Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions: EDR solutions can help detect and respond to malicious activity on endpoints, including activity related to RMM tools.
- Regularly Review Audit Logs: Review logs for unusual activity.
Key Takeaways
RMM tools are powerful tools that can be weaponized by threat actors. By implementing strong security measures, monitoring RMM tool usage, and educating users, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to these attacks. Staying vigilant and proactive is essential in today's threat landscape.
References
- DragonForce Ransomware Actors Exploits RMM Tools to Gain Acces...
- In the Wild: The latest signals from real-life threat actors
- RMM Tools Turn Rogue: How IT’s Favorite... - UNDERCODE NEWS
- Threat Actors Embed Malicious RMM Tools to... | CyberSecurityBoard
- Threat Actors Use Malicious RMM Tools for Stealthy Initial Access to...
- Ransomware Groups Weaponize RMM Tools to... - PlanetJon Network
- MSP RMM Solutions: A Full Guide to Remote Monitoring & Management





