North Korean Hackers Target Developers: Weaponizing npm for Crypto Theft
North Korean Hackers Target Developers: Weaponizing npm for Crypto Theft
The world of open-source software development is built on trust and collaboration. But what happens when that trust is exploited by malicious actors? A growing threat involves North Korean hackers who are actively weaponizing npm packages, the building blocks of JavaScript projects, to steal cryptocurrency and sensitive data from unsuspecting developers.

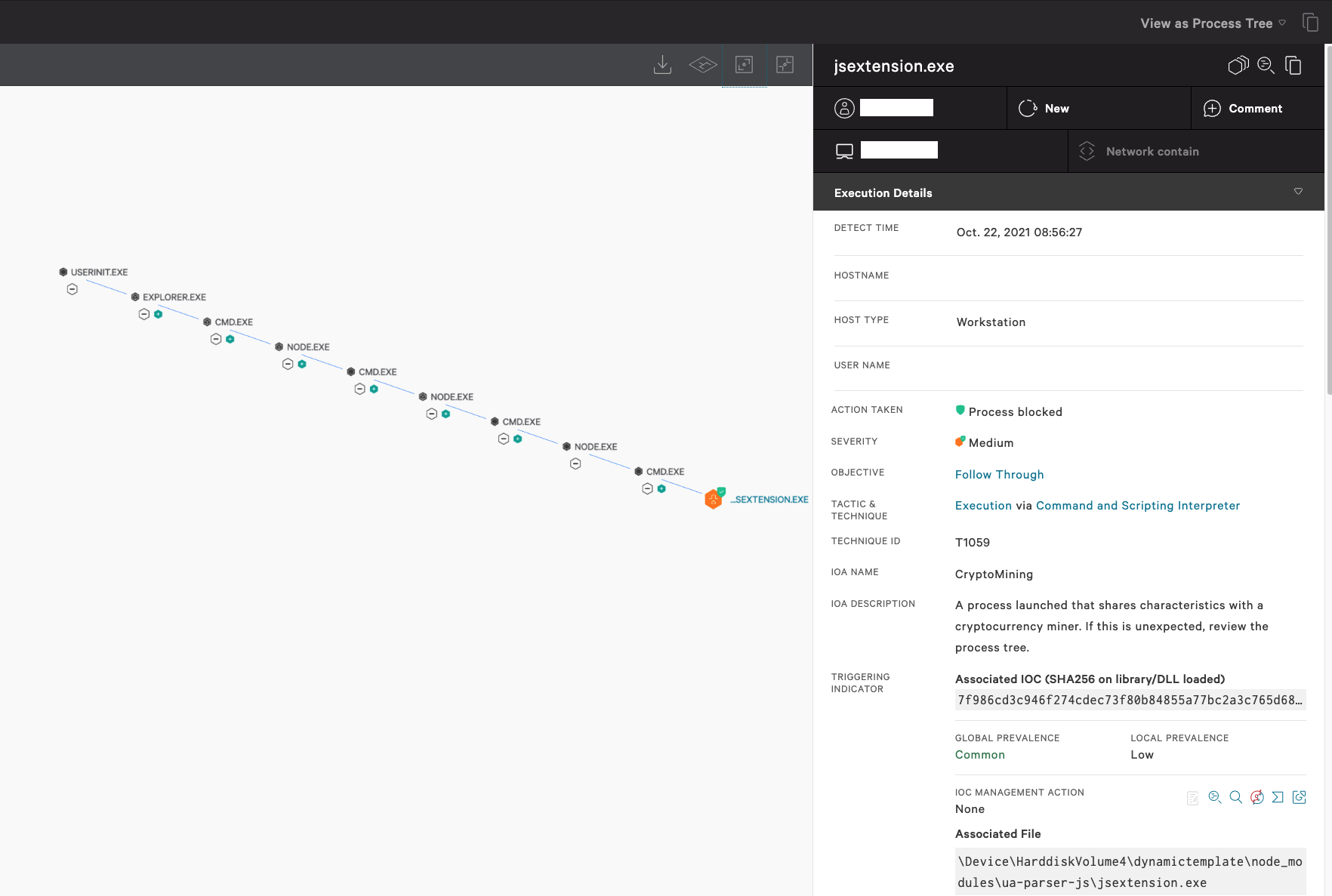
Compromised NPM Package Used in Supply Chain Attack: CrowdStrike Falcon® Customers Protected
The Threat: North Korean Hackers and npm
North Korean state-sponsored hackers have become increasingly sophisticated in their cyberattacks. One of their preferred methods is to target the software supply chain, specifically the npm (Node Package Manager) ecosystem. By injecting malicious code into popular or seemingly innocuous npm packages, they can compromise the systems of developers who use those packages in their projects.
How the Attacks Work
These attacks typically unfold in a few key stages:
- Package Infection: Hackers create or compromise npm packages, injecting malicious code designed to steal data or execute commands on the developer's machine.
- Distribution: The infected packages are then distributed through the npm registry, often disguised as legitimate tools or libraries.
- Developer Download: Unsuspecting developers download and install these packages as dependencies in their projects.
- Malware Execution: Once installed, the malicious code executes, potentially stealing cryptocurrency wallet keys, environment variables, or other sensitive information. Some attacks involve "Beavertail" malware, designed for credential theft.
- Fake Interviews: In some cases, hackers pose as recruiters and lure developers into fake job interviews. As part of the "interview" they trick the developer into installing malicious packages.
What Data is at Risk?
The primary targets of these attacks are:
- Cryptocurrency Wallet Keys: Private keys that allow hackers to access and steal cryptocurrency holdings.
- Environment Variables: API keys, database credentials, and other sensitive configuration data stored in environment variables.
- Source Code: Intellectual property that can be stolen, modified, or used to further compromise other systems.
- Credentials: Usernames, passwords, and API keys that can be used to access other systems and services.
Protecting Yourself from npm Supply Chain Attacks
While the threat is real, there are steps you can take to protect yourself and your projects:
- Be Vigilant: Carefully review the packages you are installing, especially if they are new or unfamiliar.
- Check Package Popularity and Reputation: Look for packages with a large number of downloads and positive reviews. Be wary of packages with few downloads or negative feedback.
- Use Security Tools: Employ tools like Socket to automatically analyze npm packages for security vulnerabilities.
- Implement a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM): An SBOM helps you track the components in your software and identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Monitor Network Activity: Keep an eye on your network traffic for suspicious activity, such as connections to unknown or malicious servers.
- Secure Your Environment Variables: Store sensitive information securely and avoid committing it directly to your codebase.
- Use a Virtual Machine: When evaluating new packages, consider using a virtual machine to isolate your development environment.
Key Takeaways
North Korean hackers are actively targeting developers through malicious npm packages. These attacks are designed to steal cryptocurrency and sensitive data. By being vigilant, using security tools, and following best practices, developers can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to these attacks. The open-source community must work together to identify and remove malicious packages from the npm registry and educate developers about the risks.